Common Vitreoretinal Diagnoses
Macular
Disorders affecting the central retina.
-
An acquired degeneration of the retina causing central visual impairment.
-
A thin, semi-translucent membrane on the surface of the retina affecting its architecture which may result in visual distortions and disturbances.
-
A discontinuity in the macula featuring a retinal break involving the fovea.
-
An incomplete posterior vitreous detachment with adherent vitreous exerting tractional pull on the macula which may result in decline in visual function.
-
Hyperpermeable choroidal vessels with retinal pigment epithelium dysfunction resulting in accumulation of fluid under the retina which may cause central vision decline or distortion.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Macular Pucker
Macular Hole
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
Vitreomacular Traction
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.
Vascular
Disorders affecting the arteries and/or veins of the retina.
-
Microvascular damage of the retina as a result of diabetes mellitus.
-
Vascular occlusion of a branch or central retinal vein which may result in vision loss and long-term consequences.
-
An obstruction of blood flow in a branch or central retinal artery due to a clot, inflammation, trauma or spasm.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Retinal Artery Occlusion
Retinal Vein Occlusion
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.
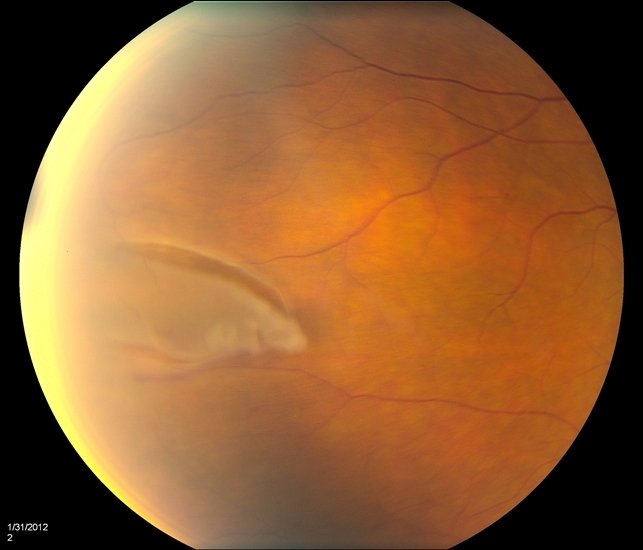
Peripheral
Disorders affecting the outermost regions of the retina.
-
Localized thinning of the peripheral retina with overlying vitreous liquefaction and vitreoretinal adhesion.
-
Full-thickness separation between the neurosensory retina and the underlying retinal pigment epithelium.
-
Full-thickness break in the neurosensory retina usually due to vitreoretinal traction.
-
Typically benign, asymptomatic, pigmented lesion of the retina.
Lattice Degeneration
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Tear
CHRPE
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.
Vitreous
Disorders affecting the gel-like material in the largest body of the eye.
-
Sensation of seeing “hairs”, “flies”, “spiderwebs” due to opacities in the vitreous body.
-
An intraocular lens which has moved out of its normal position; often into the vitreous body.
Floaters
Dislocated Intraocular Lens
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.
Inflammatory
Disorders featuring inflammation as the primary problem.
-
Inflammation affecting the middle part of the eye: the uvea (iris, ciliary body, and choroid).
-
Purulent inflammation of the intraocular fluids (aqueous and vitreous) usually due to an infection.
Uveitis
Endophthalmitis
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.
Tumors
Disorders due to abnormal growths in the choroid or retina.
-
Typically benign, asymptomatic primary intraocular tumor of the choroid.
-
A primary intraocular tumor of the choroid.
Choroidal Nevus
Choroidal Melanoma
All images were originally published in the Retina Image Bank. © the American Society of Retina Specialists.